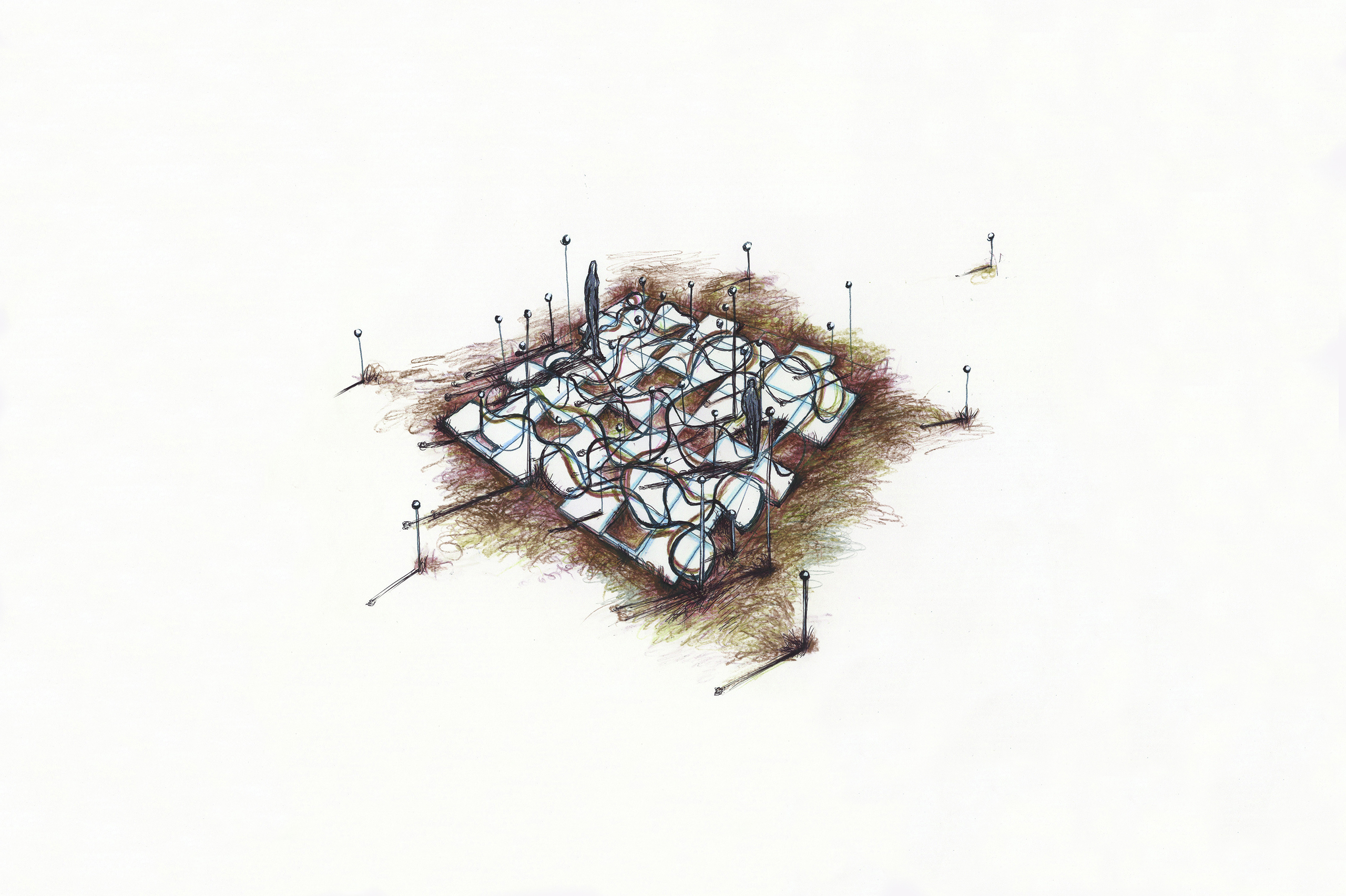
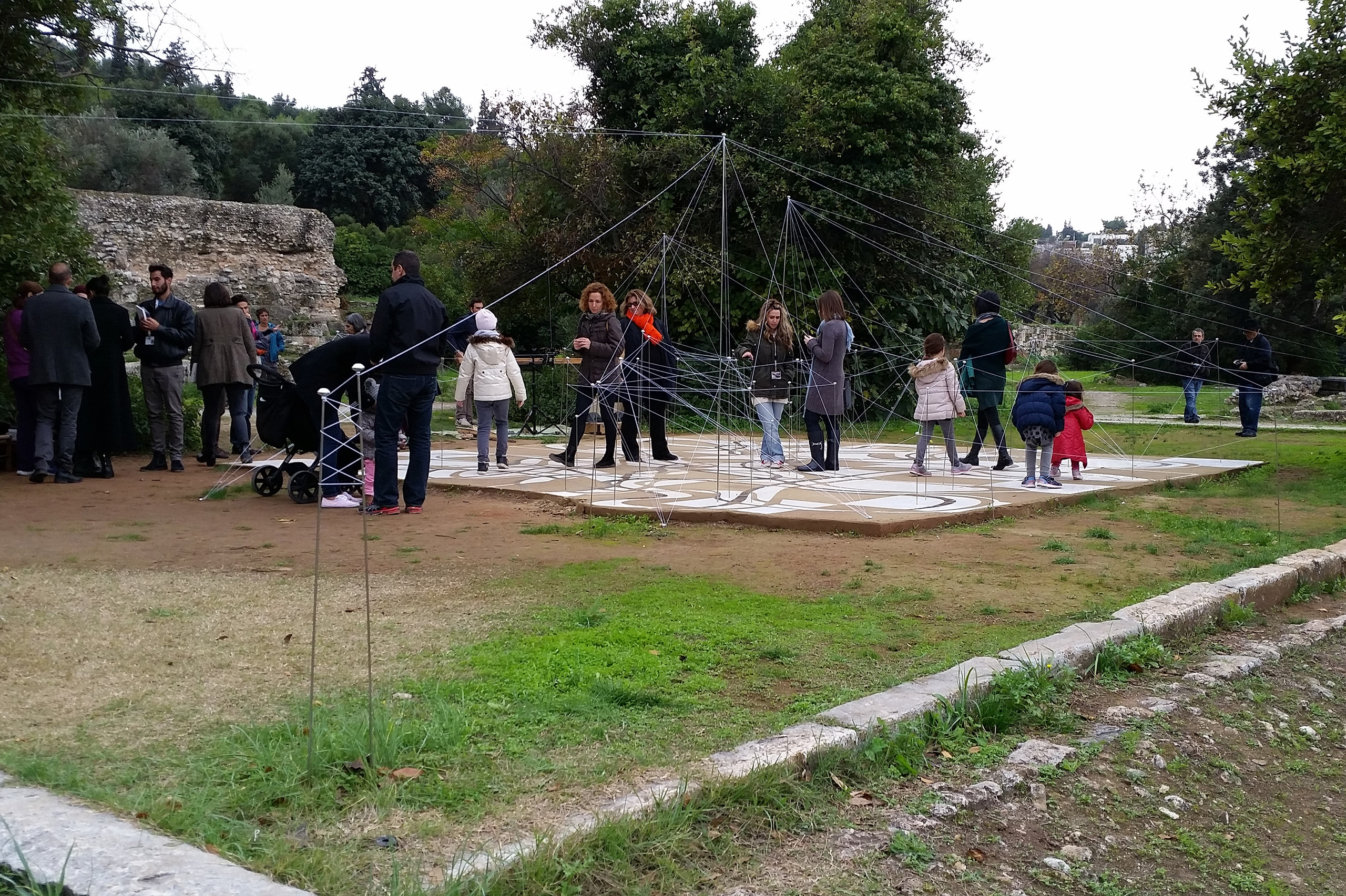
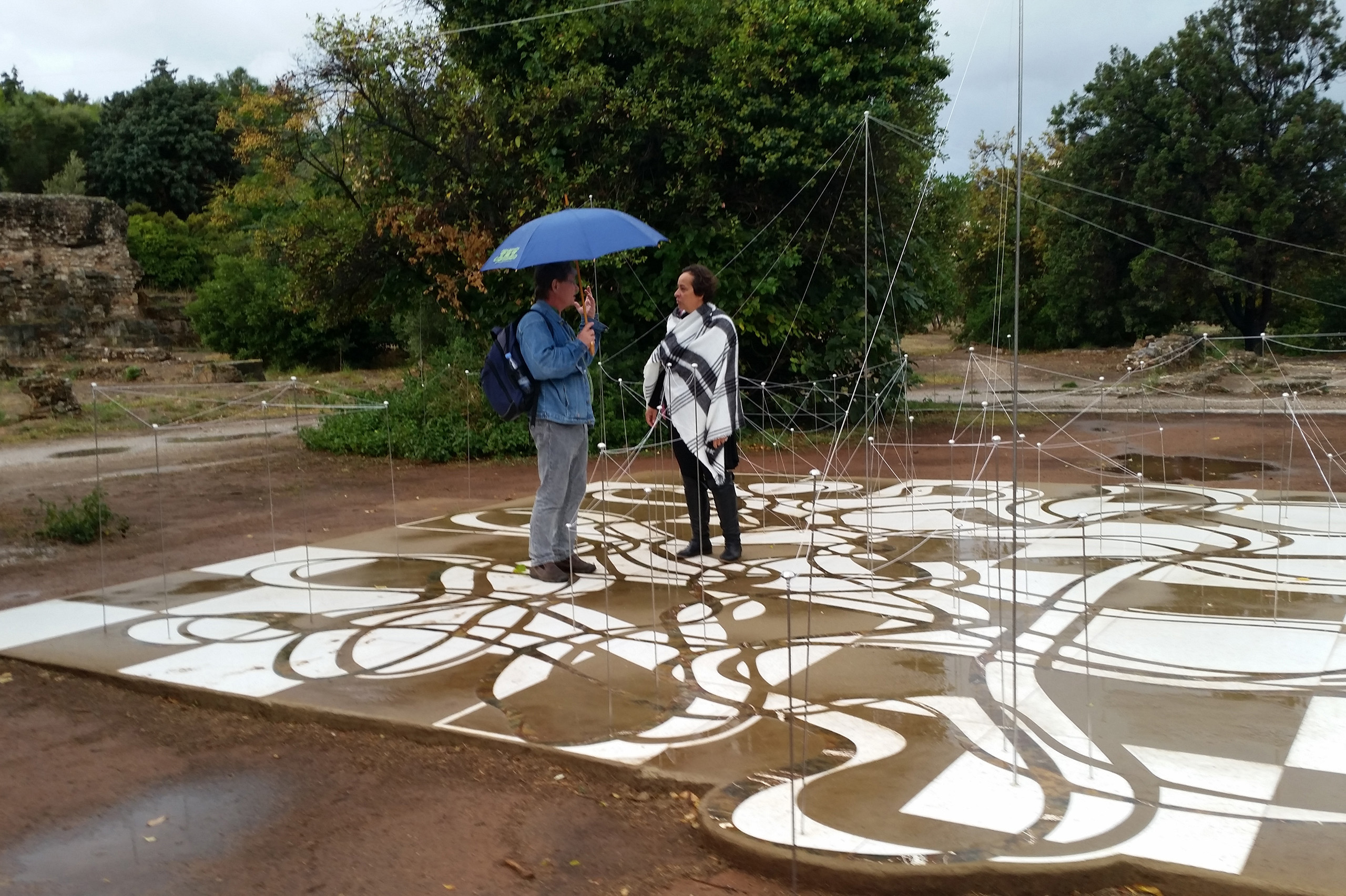
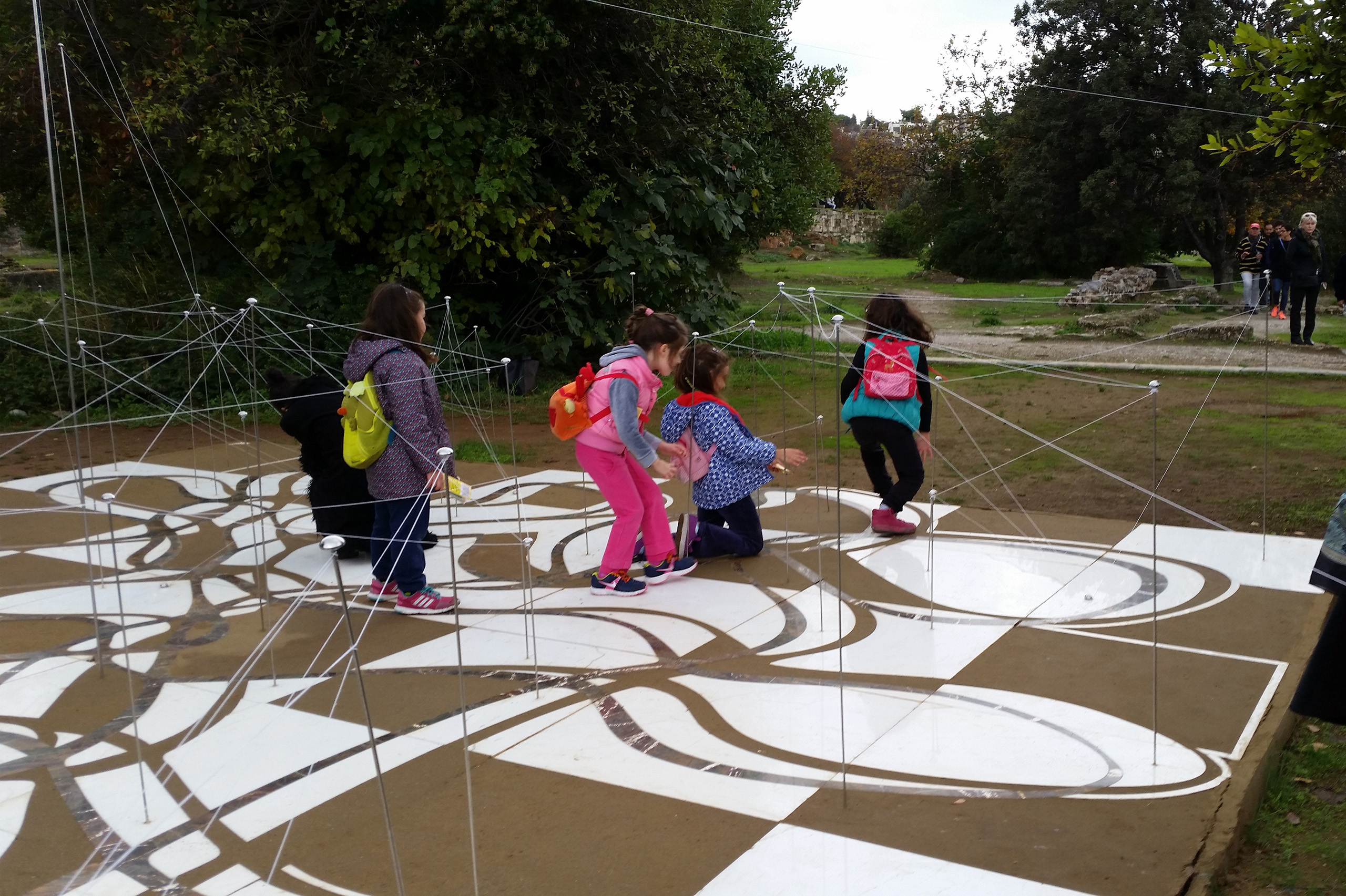
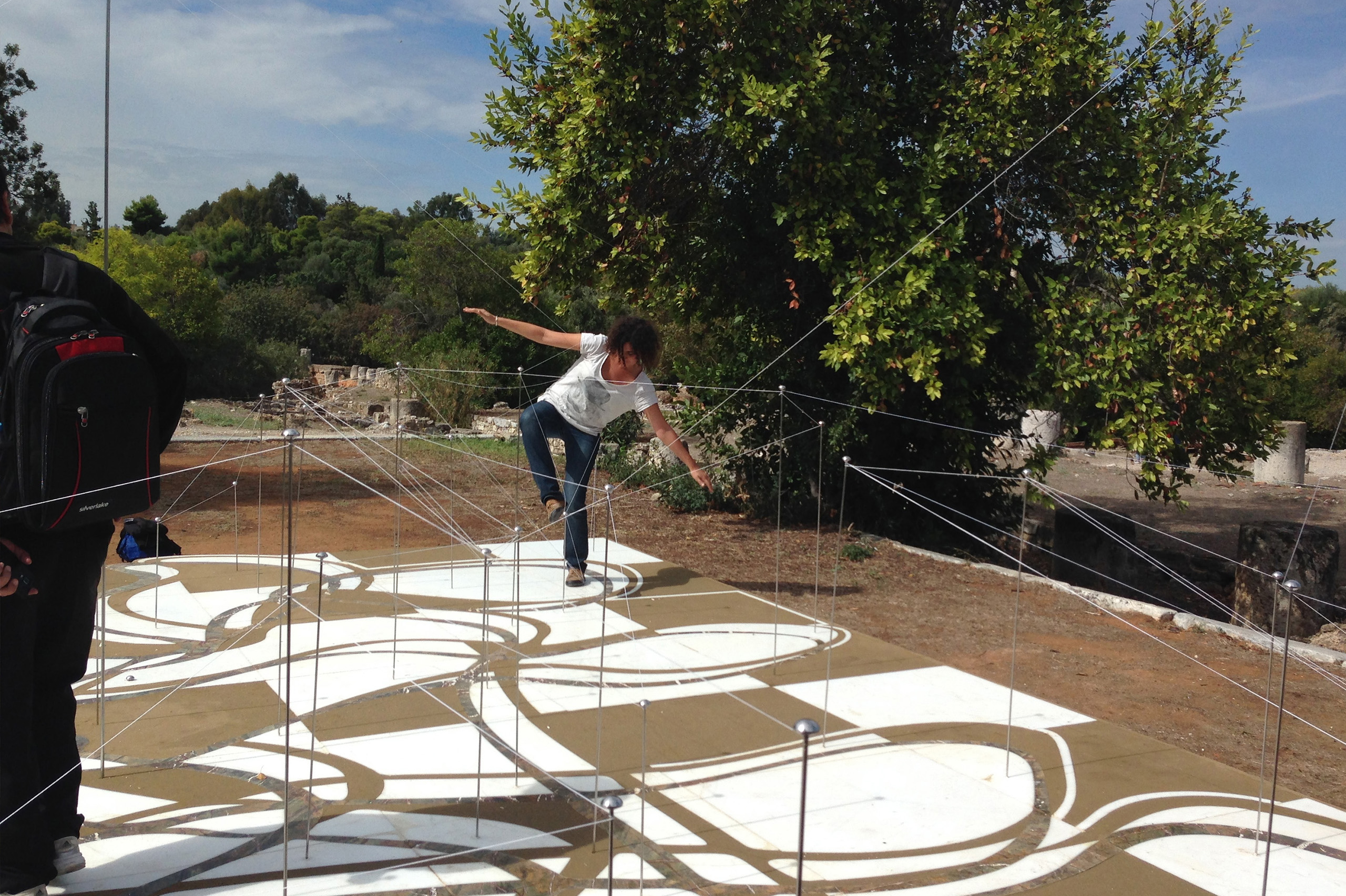
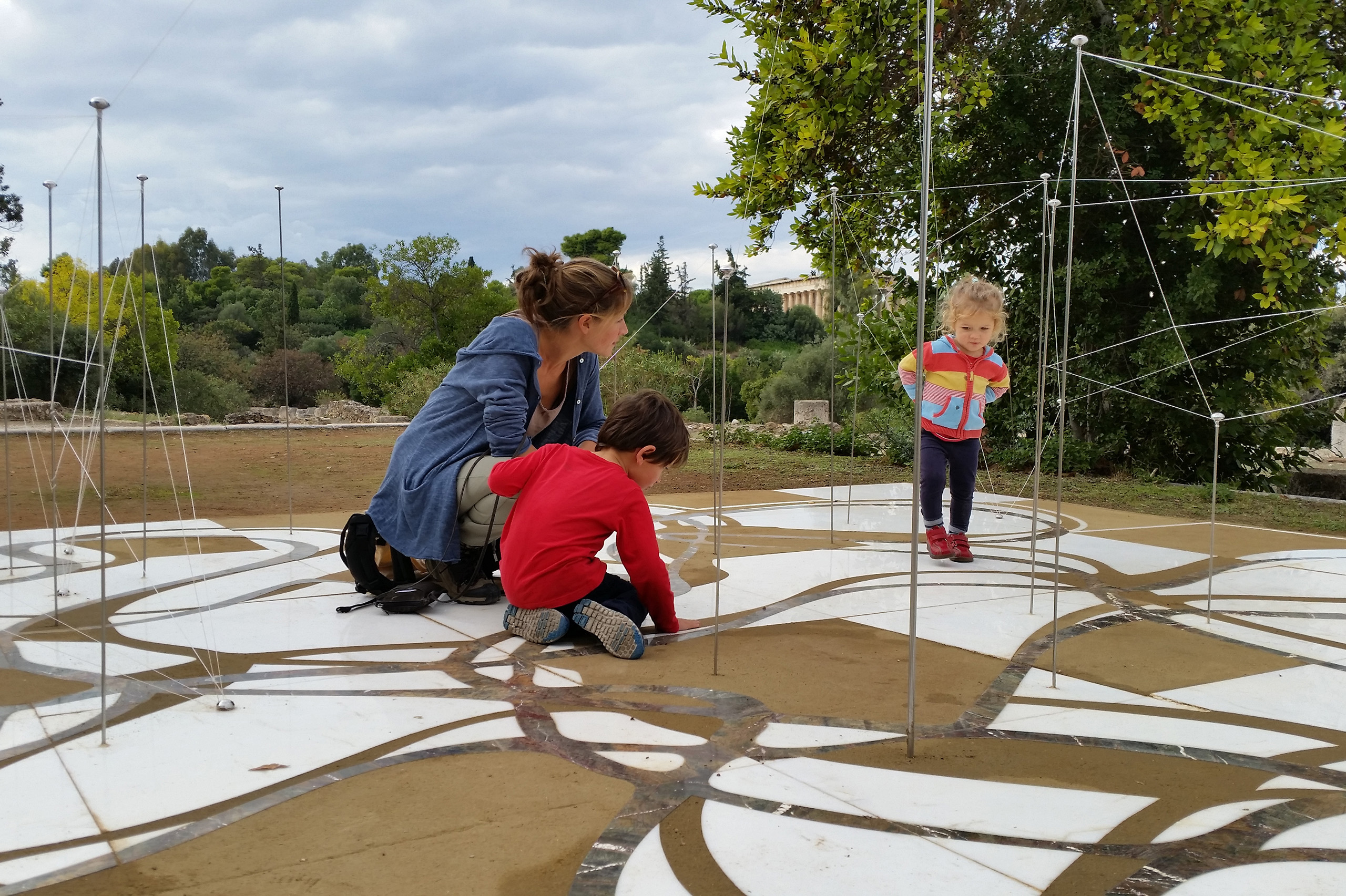
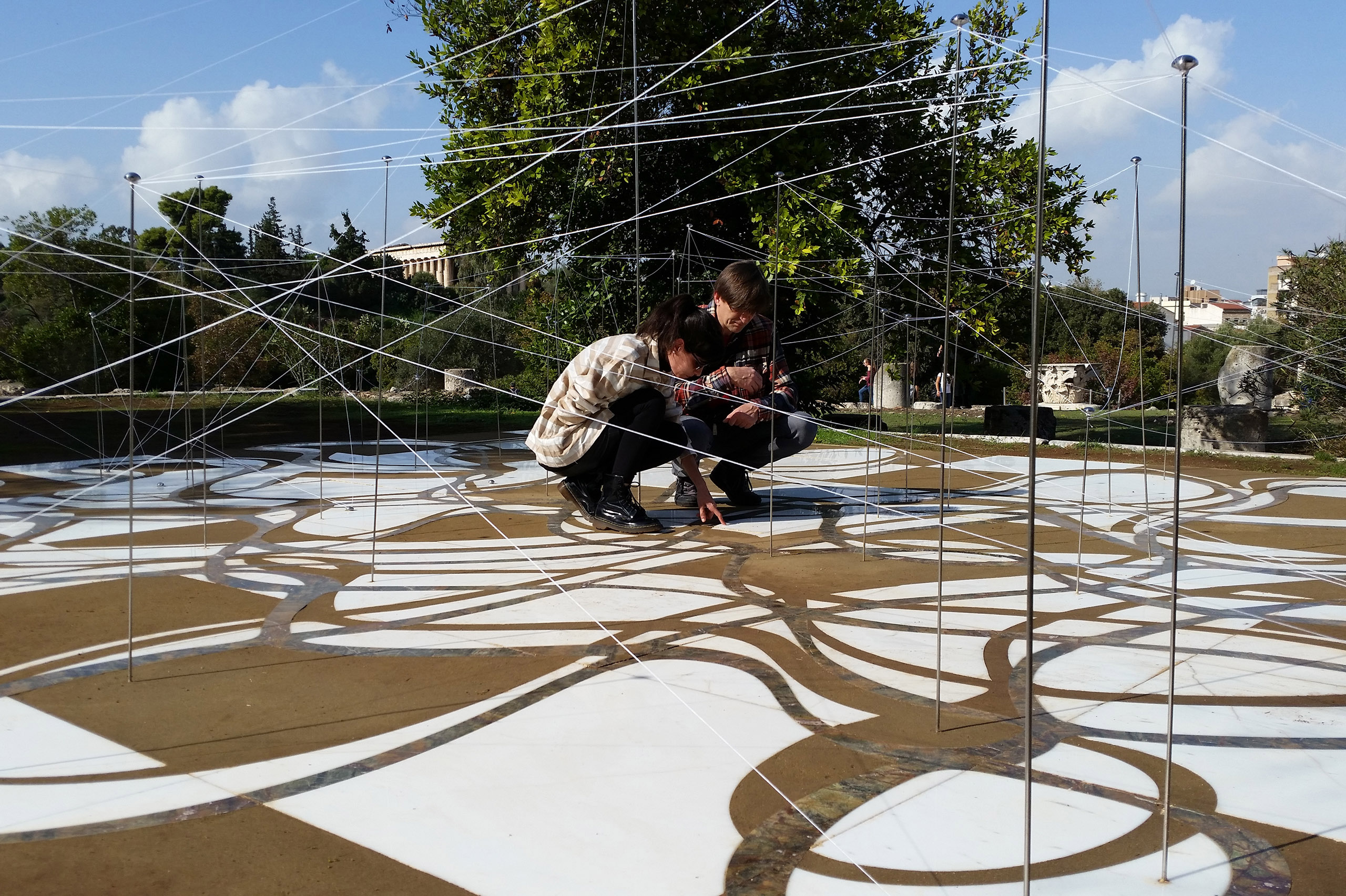
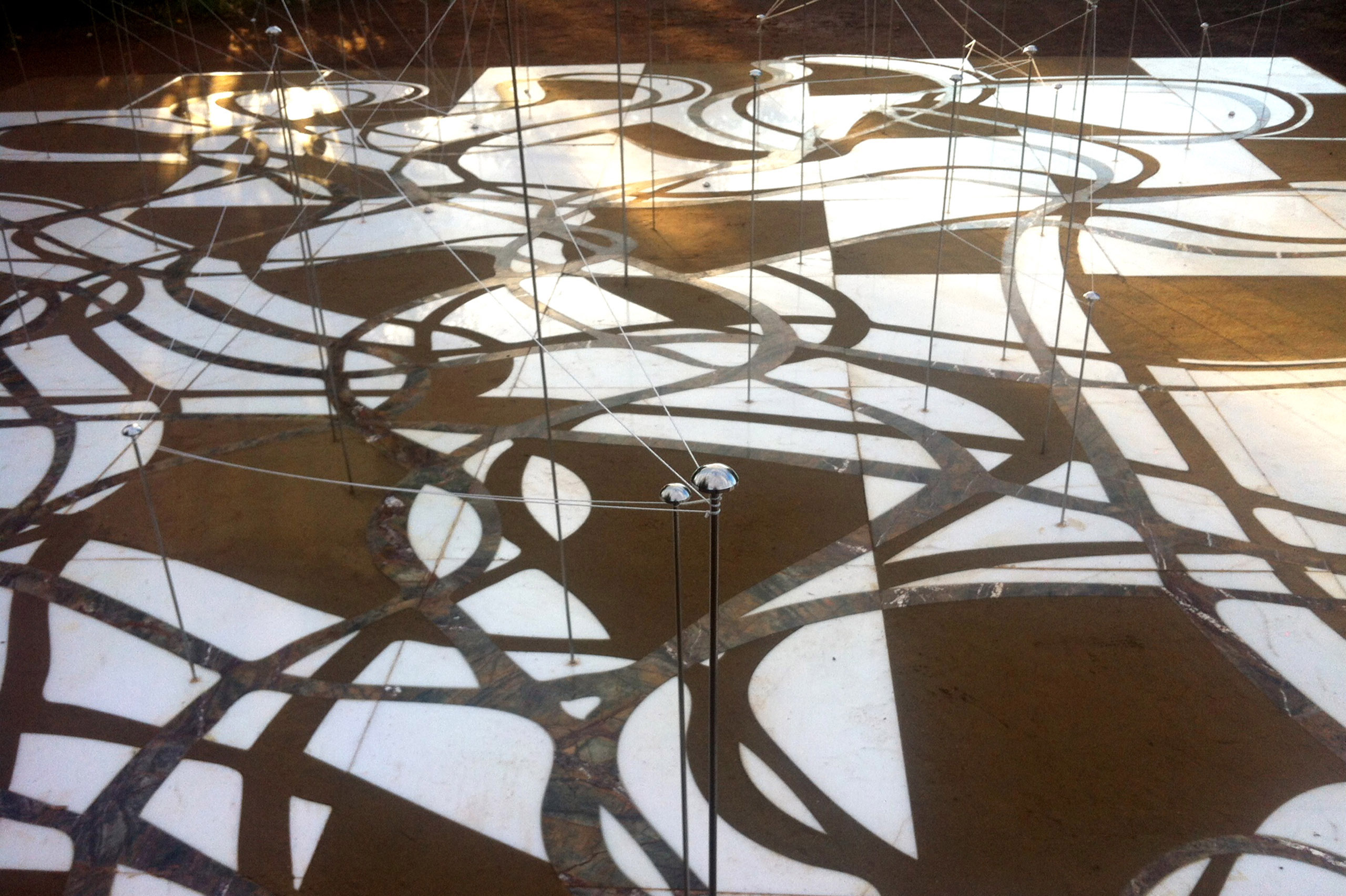
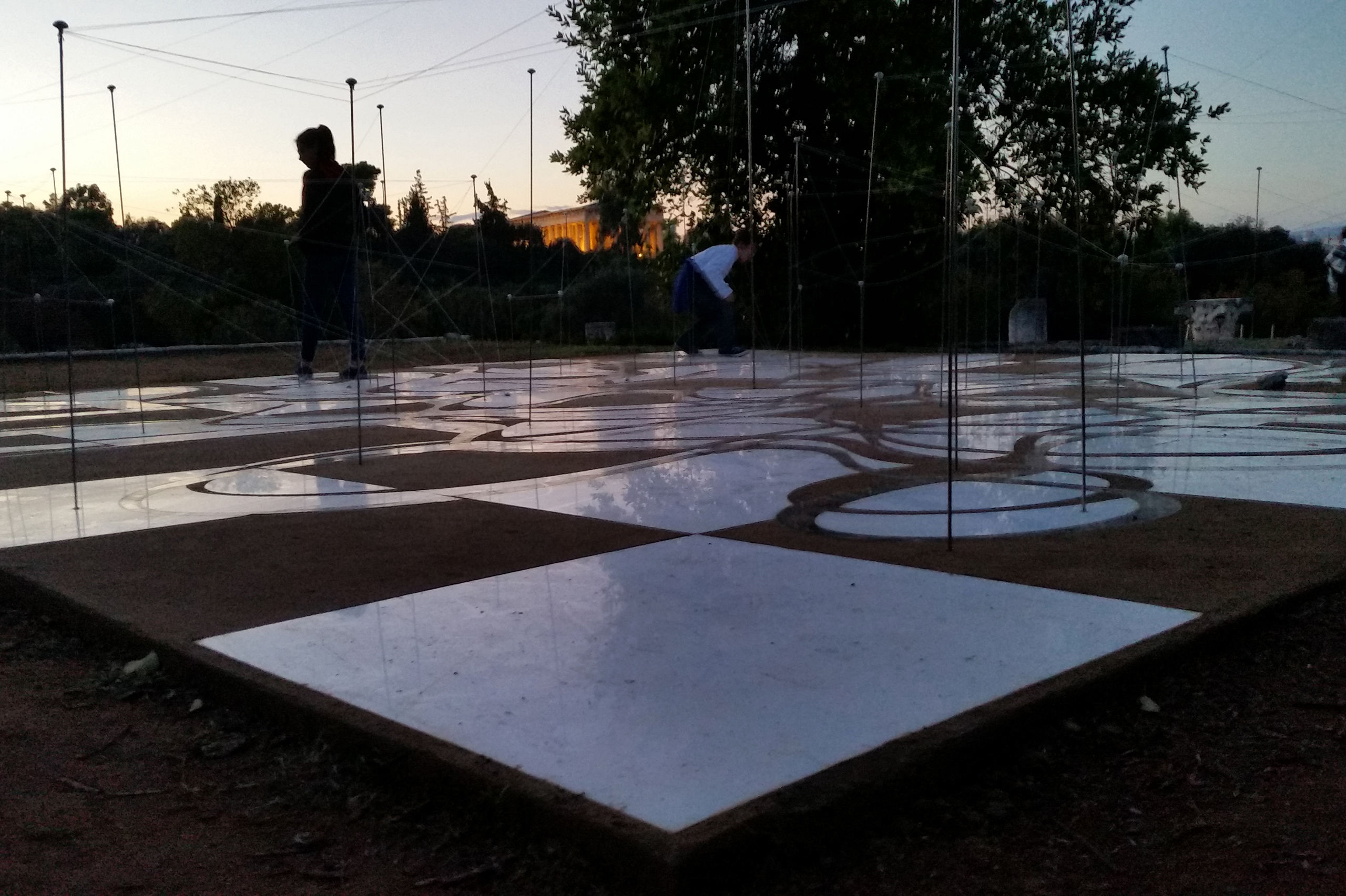
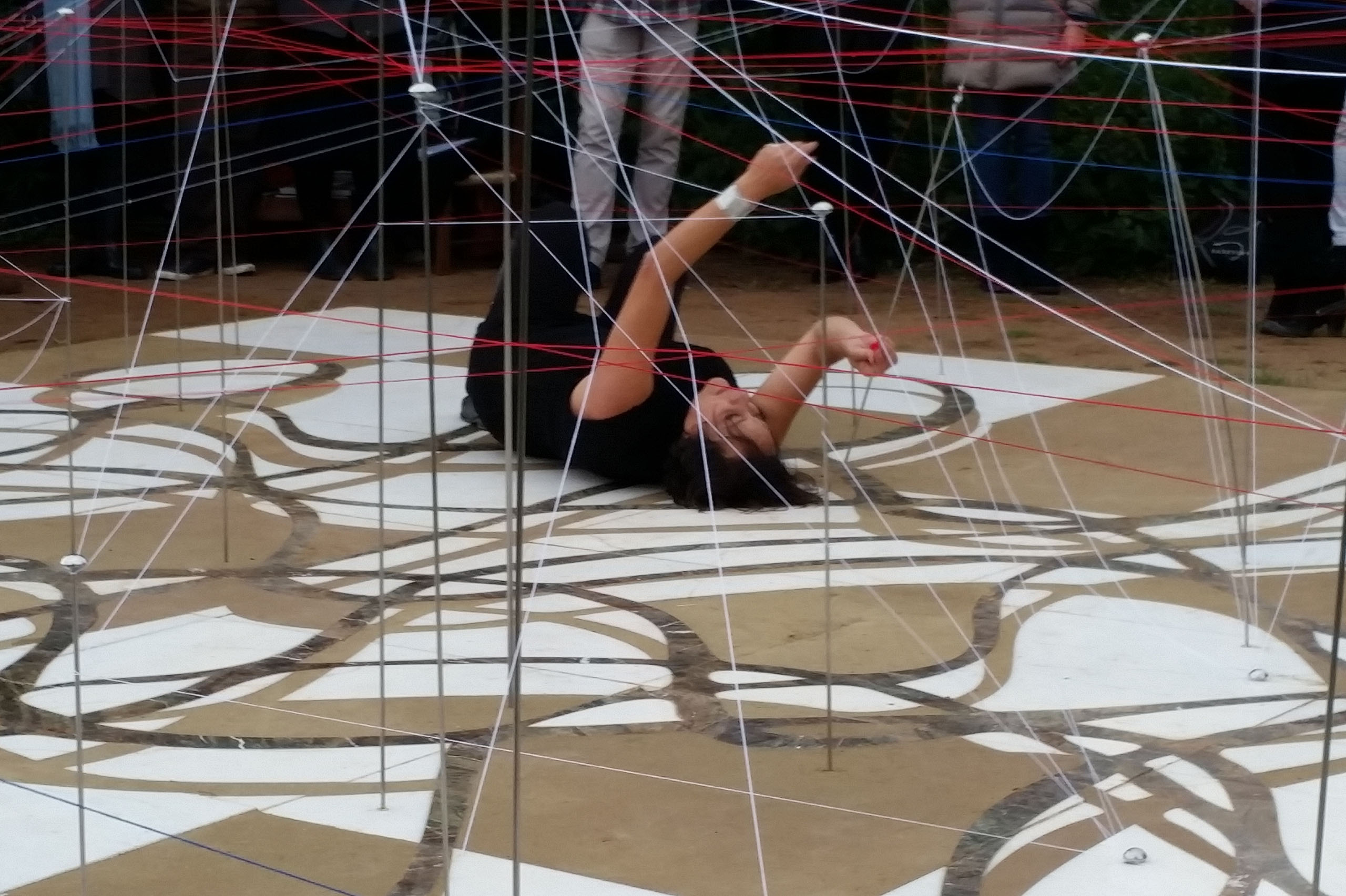
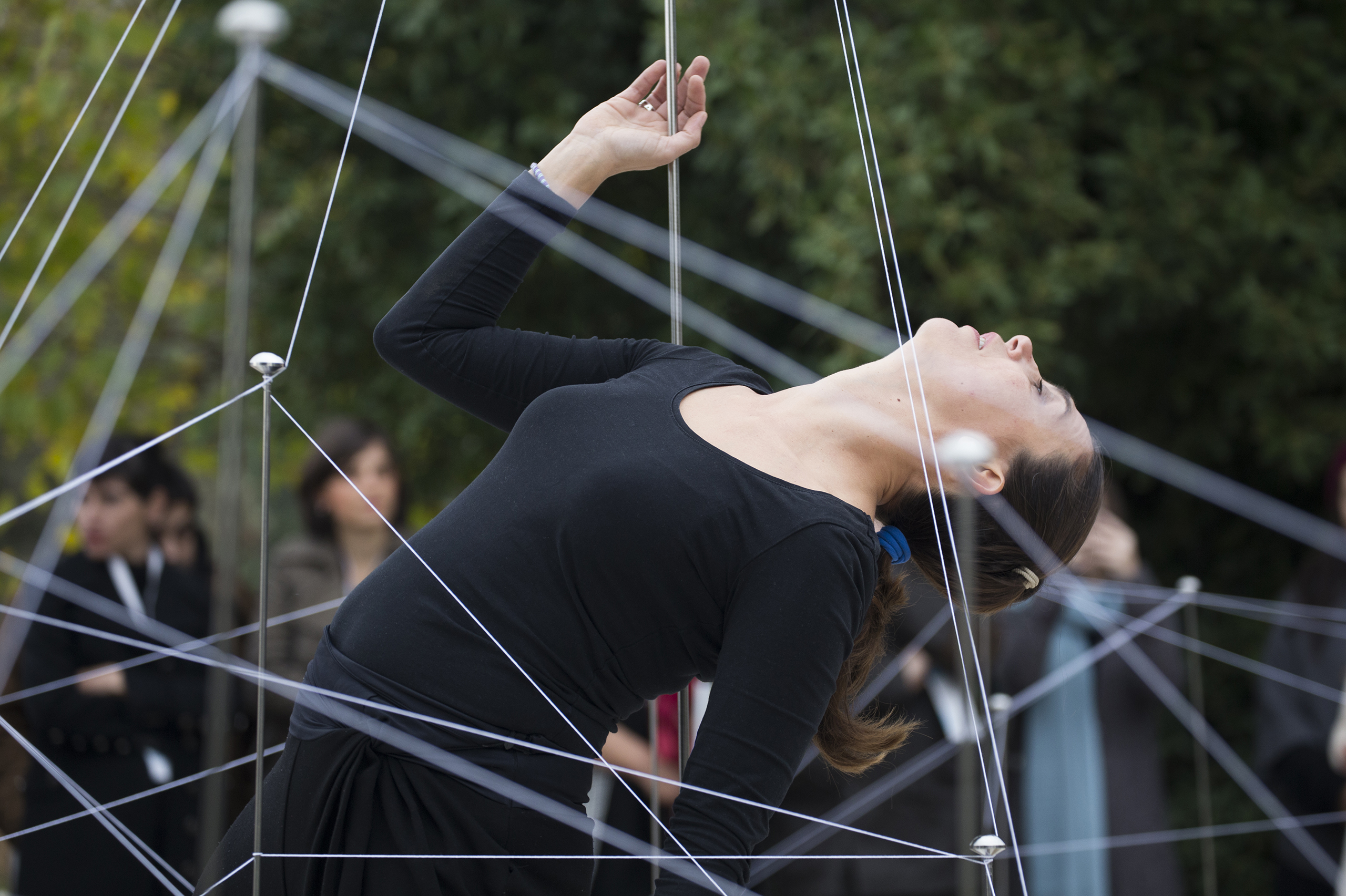
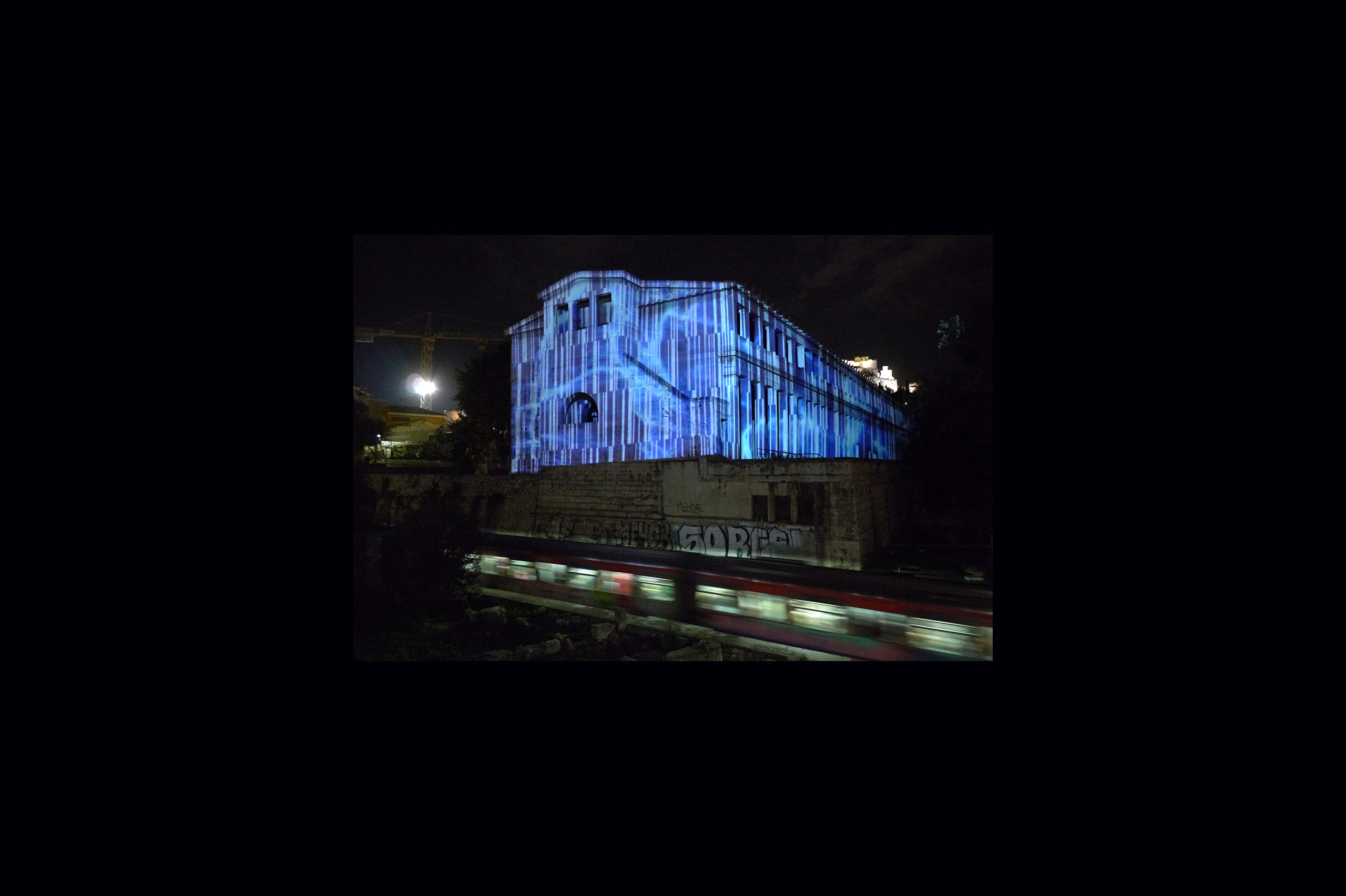
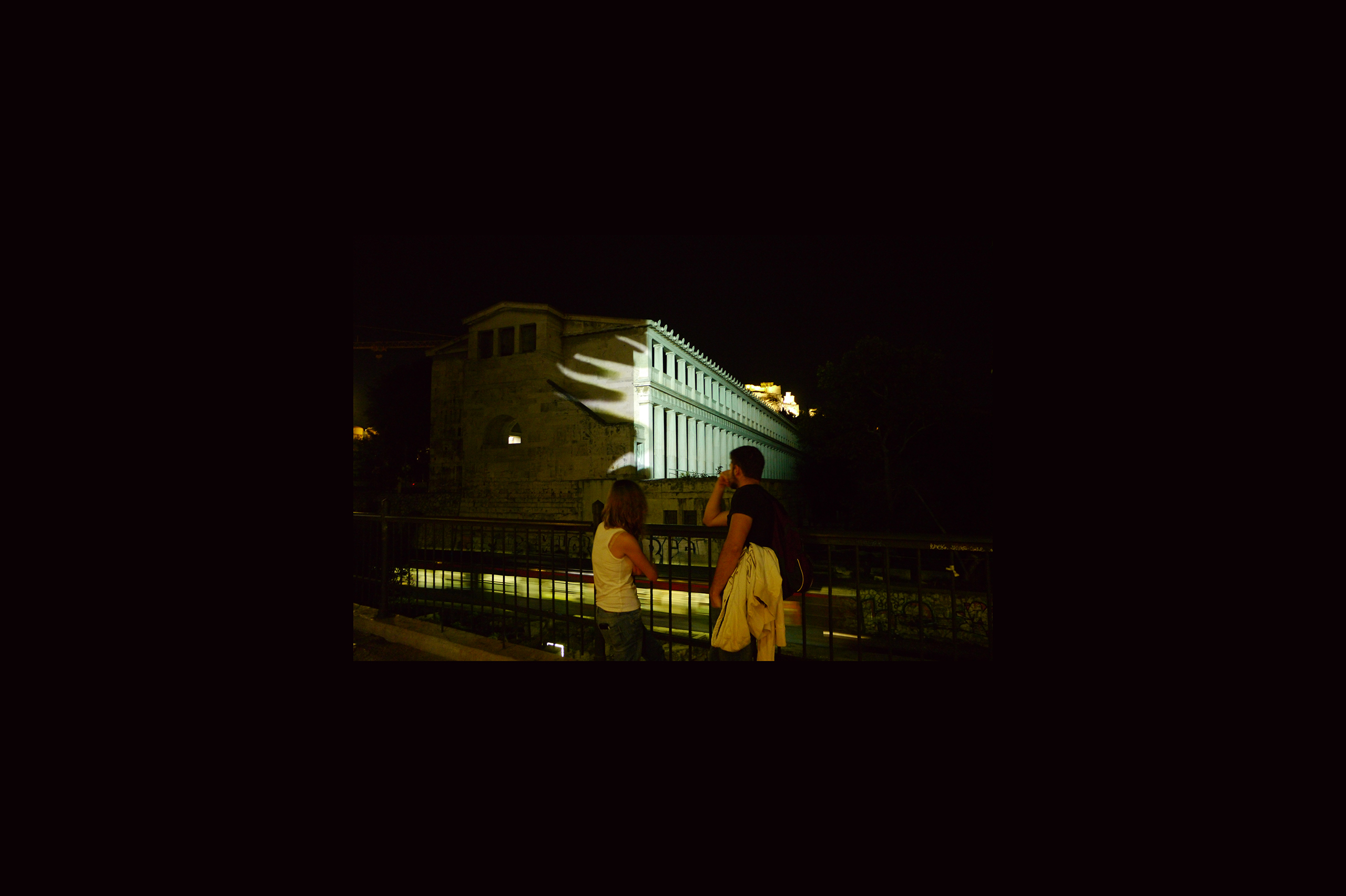
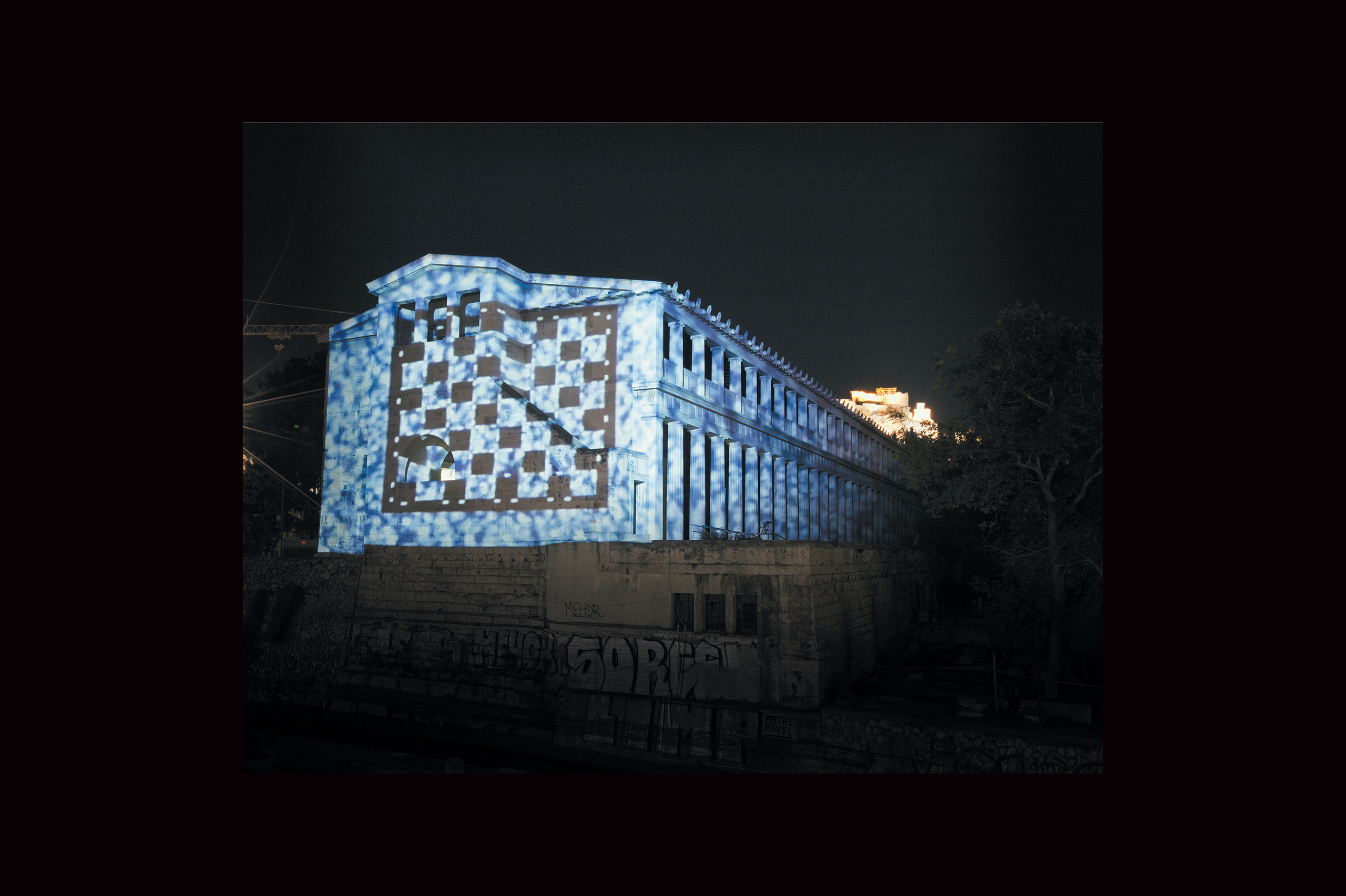
The Ancient Agora of Athens was founded during the 6th century BC and is located northwest of the Sacred Rock of the Acropolis and between the hill of Areopagus and the hill of Kolonos Agoraios. For at least the next four centuries, the Agora became the centre of the city during the Classical and Hellenistic periods. Within it, the city’s most significant public buildings and temples were erected, the Agora thereby becoming the focus of political, commercial, administrative and social activity, the religious and cultural centre, and the seat of justice. The site was occupied without interruption in all periods of the city’s history. During the years Ancient Agora of Athens faced a series of ransackings as well as periods of success until the 6th Century AD.